ZrO2 Zirconia Ceramics
Zirconia ceramic is a strong and durable material made from zirconium dioxide (ZrO2). It is highly resistant to wear and corrosion, making it ideal for use in dental implants, cutting tools, bearings, and electronic components. It is also commonly used in high-temperature applications such as furnace linings and in the aerospace and automotive industries.
ZrO2 Zirconia Ceramics

Ceramic Welding Roller

Ceramic Rod

Ceramic Ball Valve
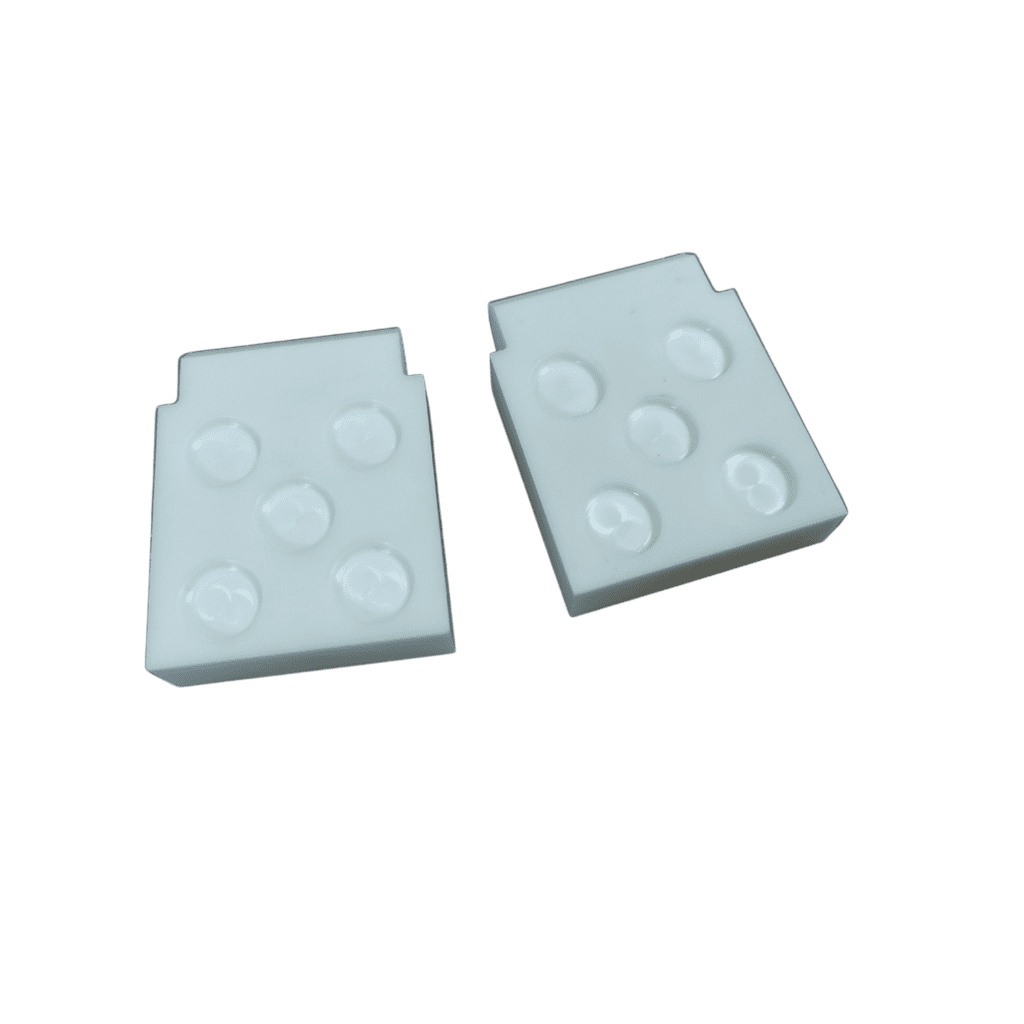
Ceramic Cutter
Details of Zirconia Ceramics
What is zirconia ceramic?
Zirconia ceramic is a type of ceramic material that is made from zirconium dioxide. It is known for its high strength, durability, and resistance to wear and corrosion.
Zirconia ceramic is often used in applications where high performance and reliability are required, such as in medical implants, dental crowns, and cutting tools. It is also used in the production of electronic components, such as capacitors and sensors.
Zirconia ceramic is a versatile material that can be shaped and molded into a variety of forms, making it a popular choice for many different industries.
Types of zirconia ceramic
There are three types of zirconia ceramics:
Partially Stabilized Zirconia (PSZ): This type of zirconia ceramic has a lower content of yttria and with a partially stabilized crystal structure, which makes it more resistant to cracking and thermal shock. It is commonly used in high-temperature applications such as furnace linings and heat exchangers.
Fully Stabilized Zirconia (FSZ): This type of zirconia ceramic has a higher content of yttria and a fully stabilized crystal structure, which makes it more resistant to wear and corrosion. It is commonly used in dental implants, artificial joints, and cutting tools.
Transformation Toughened Zirconia (TTZ): This type of zirconia is a combination of partially and fully stabilized zirconia and has a unique microstructure that allows it to resist cracking and fracture even under extreme stress. It is commonly used in aerospace and defense applications, as well as in high-performance cutting tools.
Properties of zirconia ceramic
Mian color of ZrO2 Ceramics is white. However, it can also be produced in other colors such as black, yellow, blue and pink by adding certain pigments during the manufacturing process. For example, adding yttria as a dopant can result in a white or yellow color, while adding chromium can result in a green color.
Zirconia ceramics are highly sought after for their exceptional properties that make them ideal for a wide range of applications. With a remarkable hardness rating of 8.5 on the Mohs scale, they are incredibly durable and resistant to wear, surpassing most other ceramics. Moreover, their high fracture toughness makes them less prone to cracking than other ceramics, ensuring their longevity and reliability.
Furthermore, zirconia ceramics exhibit excellent resistance to corrosion, making them a perfect choice for use in harsh environments where other materials may fail. Their biocompatibility is another significant advantage, allowing them to be used in medical implants without causing any adverse reactions in the body.
| Type | Unit | Test Standard | Zirconia | ||
| Material | ZrO₂-Y₂O₃ | ZrO₂-Mgo | Mg-Psz | ||
| Colour | white | yellow | white | ||
| Density | g/cm³ | ISO18754:2003 | 5.95-6 | 5.65 | 5.7 |
| Flexural strength | Mpa | ASTM-C1161-13 | 1000 | 480 | 580 |
| Compressive Strength | Mpa | GB/T8489-2006 | 2200 | 1600 | 1600 |
| Modules of Elasticity (young) | Gpa | ASTM-C1198-09 | 210 | 210 | 210 |
| Fracture Toughness | MPa*m1/2 | ASTM-C1421-18 | 8 | 6 | 7 |
| Poision’s Ratio | ASTM-C1421-18 | 0.3 | 0.3 | 0.3 | |
| Hardness HRA | HRA | RICKWELL 60N | 90 | 88 | 88 |
| Vickers Hardness | HV1 | ASTM-C1327-15 | 1450 | 1200 | 1200 |
| Thermal Expansion Coefficient | 10-6K-1 | ASTM-E1461-13 | 10 | 9 | 9 |
| Thermal Conductivity | W/mk | ASTM-E1461-13 | 3 | 3 | 3 |
| Thermal Shock Resistance | △T.℃ | / | 400 | 400 | 400 |
| Max Use Temperature in oxidizing Atmosphere | ℃ | NO LOAD CONDITION | 1000 | 1000 | 1000 |
| Max use Temperatur in reducing or Inert Atmosphere | ℃ | NO LOAD CONDITION | 1000 | 850 | 850 |
| Volume Resistivity at 20°C | Ωcm | / | 1012 | 5X1013 | 5X1013 |
| Dielectric Strength | kV/mm | / | 15 | 19 | 19 |
| Dielectric Constant (1MHN) | ASTM-D2149-13 | 30 | 27 | 27 | |
| Dielectric Loss Angle at 20C, 1MHz | tanδ | ASTM-D2149-13 | 2X10-3 | 2X10-3(1GHz) | 2X10-3(1GHz) |
Advantages of Zirconia Ceramics
High Strength: Zirconia ceramics have high strength and toughness, making them ideal for use in high-stress applications.
Wear Resistance: Zirconia ceramics are highly wear-resistant, making them ideal for use in applications where wear and tear are a concern.
Biocompatibility: Zirconia ceramics are biocompatible, meaning they are safe for use in medical applications such as dental implants.
Corrosion Resistance: Zirconia ceramics are highly resistant to corrosion, making them ideal for use in harsh environments.
Aesthetic Appeal: Zirconia ceramics have a natural white color that is similar to that of teeth, making them ideal for use in dental applications.
Usages of Zirconia Ceramics
Zirconia ceramic parts are a versatile solution for a wide range of industries, thanks to their exceptional mechanical, thermal, and chemical properties. These parts are highly sought after for their biocompatibility, resistance to wear and corrosion, and high hardness. But how could us choose the right part for our application, here are some of the specific applications where Zirconia ceramic parts excel:
Medical implants: Dental implants, hip and knee replacements, and other orthopedic implants rely on Zirconia ceramic parts for their biocompatibility and durability.
Cutting tools: Knives, scissors, and blades benefit from Zirconia ceramic parts’ high hardness and wear resistance.
Aerospace industry: Zirconia ceramic parts are used in turbine blades, heat shields, and engine components due to their high strength and thermal stability.
Electronics industry: Insulators, capacitors, and sensors in the electronics industry rely on Zirconia ceramic parts for their high dielectric strength and thermal stability.
Automotive industry: Engine components, exhaust systems, and brake pads in the automotive industry benefit from Zirconia ceramic parts’ high strength and wear resistance.
Provide ON-SITE GUIDANCE for orders over $300,000
Compared to steel, technical ceramics have the potential to significantly increase the lifespan of equipment and enhance product precision
The whole production processes of Zirconia Ceramics
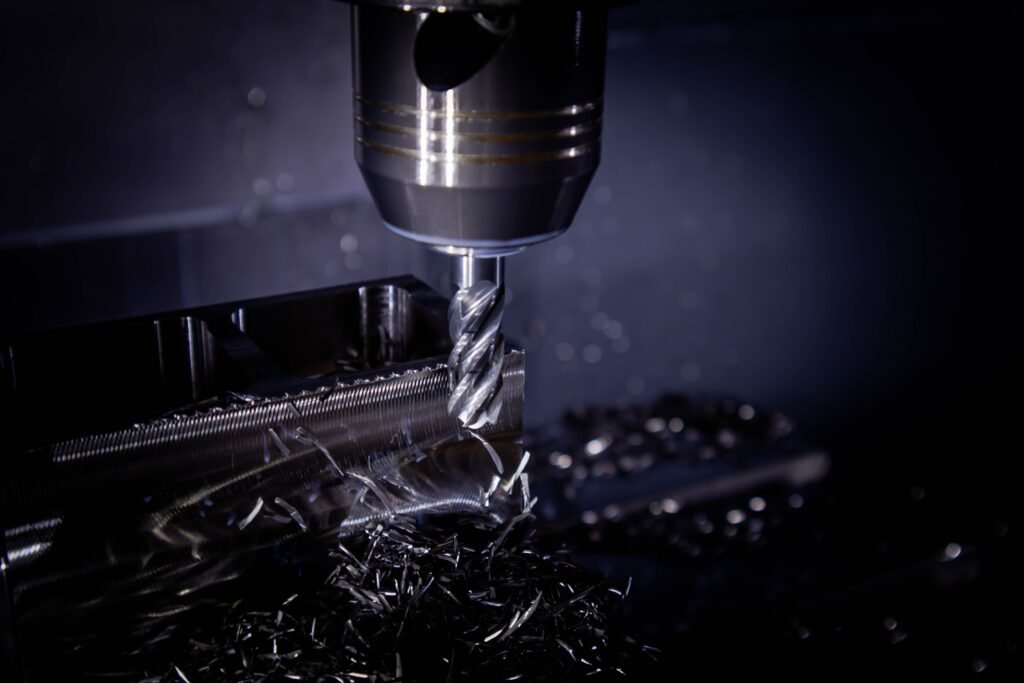
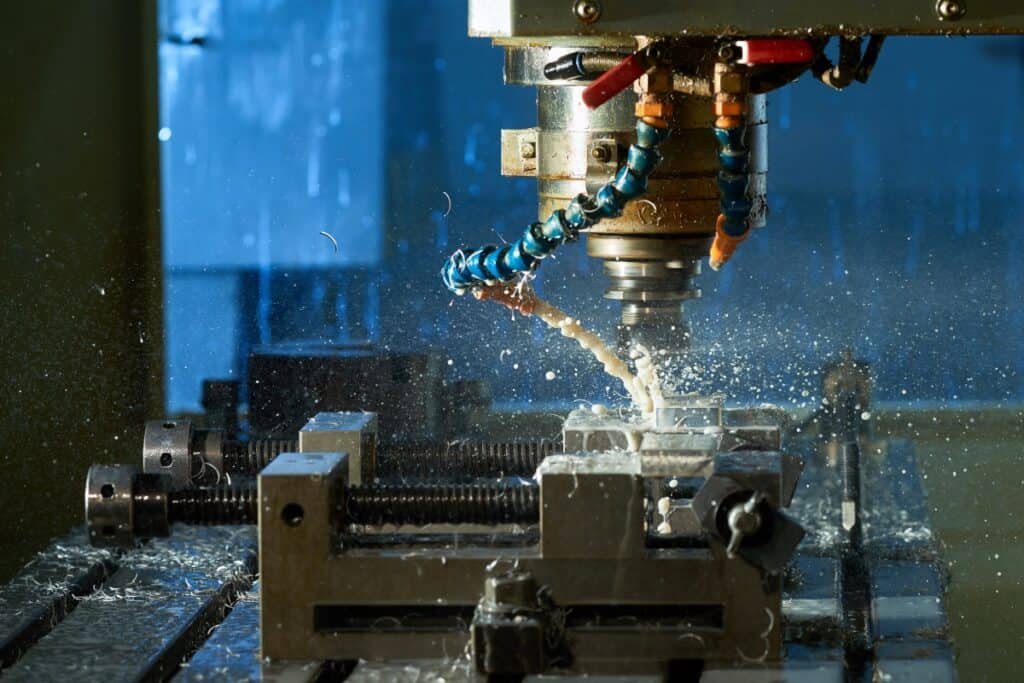


Shaping
Zirconia powder is mixed with a binder and shaped into the desired form using a process such as injection molding, extrusion, or isostatic pressing. The binder is then removed by heating the part to a high temperature.
Sintering
The shaped zirconia part is then sintered at a high temperature to fuse the zirconia particles together and achieve the desired density and mechanical properties. The sintering process typically involves heating the part to a temperature between 1400°C and 1700°C for several hours in a controlled atmosphere.
Machining
After sintering, the zirconia ceramic part may require additional machining to achieve the desired dimensions and surface finish. This can be done using techniques such as grinding, milling, or polishing.
Finishing
Finally, the zirconia ceramic part may be finished by coating, glazing, or decorating it as needed.
Quality Check
After finishing all the production precesses, the parts will be checked one by one to keep them are free from defects, errors, or any other issues that may affect their performance or functionality.
Is It Good As Metals? Things You Need To Know
To save you from worries, here are some facts you need to know about our advanced ceramic parts supplies:
High Temperature Resistance
Advanced ceramics can withstand higher temperatures than most metals, making them ideal for use in high-temperature applications.
Hardness And Wear Resistance
Structural ceramics are much harder and more wear-resistant than metals, making them ideal for use in applications where wear and tear are a concern.
Corrosion Resistance
Ceramics are highly resistant to corrosion, making them ideal for use in harsh environments where metals would quickly corrode.
Electrical Insulation
Ceramics are excellent electrical insulators, making them ideal for use in electrical and electronic applications.
Biocompatibility
Some advanced ceramics are biocompatible, meaning they can be used in medical applications without causing harm to the body.
Lightweight
Ceramics are generally lighter than metals, making them ideal for use in applications where weight is a concern.
Low Thermal Expansion
Ceramics have a low coefficient of thermal expansion, meaning they do not expand or contract significantly with changes in temperature, making them ideal for use in precision applications.




